Introduction To apache superset 4.0.2 change language default
Apache Superset is a powerful, open-supply platform designed for information exploration and visualization. It empowers users to craft dynamic dashboards, insightful reviews, and visually enticing information representations readily. Known for its versatility and scalability, Superset has come to be a preferred device for agencies and analysts who require real-time statistics insights supplied in an intuitive format.
With the release of Version 4.Zero.2, Apache Superset takes a tremendous leap forward in enhancing consumer experience and accessibility. One standout improvement is the creation of customizable default language settings. This characteristic caters to a diverse worldwide target market, allowing customers to switch to their desired language and enjoy a extra localized and personalized enjoy.
By prioritizing such updates, Apache Superset keeps to solidify its position as a user-pleasant and inclusive platform that meets the growing demands of information visualization in nowadays’s multilingual and numerous international.
How to Configure Language Settings in Apache Superset 4.0.2: A Comprehensive Guide
Apache Superset is a effective open-source statistics exploration and visualization device, relied on via agencies global for its flexibility and scalability. Among its key capabilities, the ability to customize language settings stands out, specially with the discharge of model four.0.2. This replace enables customers to set and alter default language alternatives, improving accessibility and person delight for various, worldwide audiences.
This manual explores the step-by way of-step procedure of configuring language settings in Apache Superset, the broader implications of localization in information analytics, and nice practices for maximizing these functions.
Understanding Language Configuration in Apache Superset
The capability to customize the language settings in Apache Superset is facilitated by way of the superset_config.Py report. This configuration report is principal to tailoring the platform’s functionality, allowing customers to modify not only language options but additionally aspects like security, caching, and records connectors.
Key Features of Language Configuration
Default Language Setting: Defines the language used across the platform’s interface.
User-Specific Localization: Allows individuals to choose their preferred language.
Customization Options: Facilitates the addition of new language packs and ensures adaptability for various user demographics.
Step-by-Step Guide to Change the Default Language
Step 1: Locate the Configuration File
The configuration file, superset_config.py, is typically found in the root directory of your Apache Superset installation. If it doesn’t exist, you can create it by copying the default config.py file included in the Superset package.
Step 2: Edit the Configuration File
Open the file in a text editor like Vim, Nano, or any IDE of your choice. Navigate to the section that pertains to localization and language settings.
Step 3: Modify the Default Language
This example sets French as the default language. Replace fr with the appropriate code for your desired language, such as es for Spanish or de for German.
Step 4: Restart Apache Superset
After saving your changes, restart the Apache Superset server to apply the new language settings. In the terminal, type the following command:
Step 5: Verify the Changes
Log into Apache Superset via a web browser and confirm that the interface reflects the new language configuration.
Expanding Language Options in Apache Superset
Apache Superset 4.0.2 goes beyond allowing users to change the default language—it also supports the addition of new language packs. This feature is invaluable for organizations serving diverse user bases.
Adding New Language Packs
Contribute to Translations: Submit new translations through Apache Superset’s GitHub repository.
Test Thoroughly: Ensure all text elements, including menus and error messages, appear correctly in the new language.
Integrate Seamlessly: Once validated, incorporate the language pack into your Superset environment for production use.
Enhancing User Experience Through Localization
Language settings are more than a convenience—they’re a strategic feature that enhances user satisfaction and engagement. Here’s how localized settings improve the user experience:
Accessibility: By offering multiple language options, users can navigate the platform comfortably, regardless of their linguistic background.
Cultural Relevance: Localized formats for dates, numbers, and currencies ensure the interface aligns with regional conventions.
Improved Adoption: Teams and clients are more likely to embrace a tool that caters to their language preferences.
Best Practices for Language Configuration
To maximize the benefits of Apache Superset’s language settings, consider these best practices:
Understand Your Audience
Analyze user demographics to identify the most relevant languages. Tailor your configuration to meet the preferences of your primary audience.
Enable Dynamic Language Selection
Allow users to switch languages dynamically, ensuring flexibility in diverse environments.
Perform Localization QA
Test the interface thoroughly in each language to ensure accuracy and contextual appropriateness.
Train Users
Provide training sessions or resources to help users navigate localized interfaces effectively.
Update Support Materials
Ensure that documentation and help guides are available in all supported languages.
Real-World Impact of Localization
Many organizations have reported significant improvements in engagement and efficiency after implementing language localization:
Increased Adoption: A global IT company saw a 40% rise in platform adoption by offering interfaces in key regional languages.
Reduced Support Tickets: A logistics firm reduced UI-related support requests by 70% after switching to users’ native languages.
SEO Benefits of Multilingual Platforms
Optimizing language settings can also enhance search engine visibility, helping organizations attract a global audience.
Region-Specific Search Rankings: Localized content ranks higher in region-specific search results.
Improved User Retention: Visitors are more likely to return to a platform that caters to their language preferences.
Preparing for the Future of Localization in Analytics
The future of data visualization tools like Apache Superset lies in advanced localization capabilities:
AI-Driven Translations: Dynamic translation tools powered by AI could provide real-time language adaptation.
Hybrid Multilingual Dashboards: Interfaces that display data labels and content in multiple languages simultaneously.
Geolocation-Based Recommendations: Personalized language suggestions based on user location.
How to Configure Language Settings in Apache Superset 4.0.2: A Comprehensive Guide
Apache Superset is a effective open-source statistics exploration and visualization device, relied on via agencies global for its flexibility and scalability. Among its key capabilities, the ability to customize language settings stands out, specially with the discharge of model four.0.2. This replace enables customers to set and alter default language alternatives, improving accessibility and person delight for various, worldwide audiences.
This manual explores the step-by way of-step procedure of configuring language settings in Apache Superset, the broader implications of localization in information analytics, and nice practices for maximizing these functions.
Understanding Language Configuration in Apache Superset
The capability to customize the language settings in Apache Superset is facilitated by way of the superset_config.Py report. This configuration report is principal to tailoring the platform’s functionality, allowing customers to modify not only language options but additionally aspects like security, caching, and records connectors.
Step 2: Define the Default Language
Modify the BABEL_DEFAULT_LOCALE Setting
In the superset_config.py file, locate or add the following line to define the default language:
Step 3: Restart the Superset Server
After saving your changes, restart the Apache Superset server to apply the new settings. Use the following commands to stop and start the server:
Step 4: Verify the Changes
Log in to your Apache Superset instance and navigate through the interface. Confirm that menus, labels, and other text elements are displayed in the selected default language. If the changes are not reflected, revisit the configuration file and confirm that the BABEL_DEFAULT_LOCALE value is correctly set.
Optional: Enable User-Specific Language Preferences
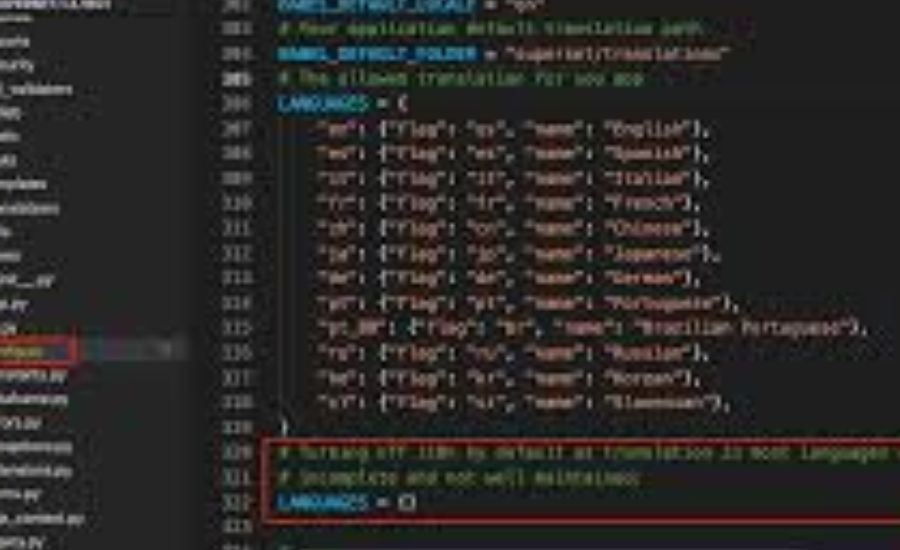
For groups with numerous person bases, it could be high-quality to allow customers to choose their desired language dynamically. To guide a couple of languages, replace the LANGUAGES setting within the superset_config.Py report:
This setup gives flexibility for users to customise their revel in while maintaining a worldwide reach.
Why Changing the Default Language Matters
The ability to exchange the default language in Apache Superset is greater than a comfort; it’s a need in today’s globalized surroundings. Here’s why:
1. Enhanced Accessibility
By supplying localized interfaces, corporations ensure that non-English speakers can easily navigate the platform. This fosters inclusivity and empowers all customers to make the most of Superset’s effective features.
2. Improved User Engagement
Users are much more likely to discover and adopt a platform when it’s to be had in their native language. A localized interface reduces cognitive load, making it simpler to recognize and utilize complex equipment.
Three. Increased Productivity
Switching the default language to align with person alternatives minimizes confusion and mistakes, permitting groups to cognizance on their analytical obligations without language obstacles.
4. Global Reach
For multinational groups, supplying a couple of language alternatives strengthens logo agree with and complements client satisfaction.
Challenges and Troubleshooting
While configuring the default language in Apache Superset is straightforward, a few challenges may arise:
1. Incomplete Translations
Not all languages may be fully supported in every feature. Organizations can contribute translations to the Apache Superset project to improve language coverage.
2. Server Errors
If the application fails to start after updating the configuration, review the server logs for potential syntax errors or compatibility issues.
3. Language Mismatch
Ensure that the BABEL_DEFAULT_LOCALE value matches the language codes supported by Superset.
Best Practices for Language Configuration
Know Your Audience
Analyze your user demographics to identify the most commonly spoken languages. This ensures that the default language resonates with the majority of your users.
Perform Localization Testing
After configuring the language settings, test the interface to confirm that translations are accurate and contextually appropriate.
Provide Support Materials
Create user guides, tutorials, and FAQs in multiple languages to complement the localized interface.
Encourage Feedback
Establish a feedback loop to identify and address issues with language settings, ensuring continuous improvement.
Real-World Benefits of Language Localization
Many organizations have experienced significant improvements in user satisfaction after implementing language localization. For example:
A global e-commerce platform saw a 40% increase in user retention after adding support for 10 major languages.
A logistics company reduced support requests by 60% by offering multilingual dashboards tailored to its international workforce.
Future Trends in Language Customization
With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, language localization in platforms like Apache Superset is expected to evolve further:
Dynamic AI Translations: User interfaces could automatically adjust language preferences in real-time based on user behavior.
Hybrid Multilingual Dashboards: Future updates may enable hybrid content, allowing elements like labels and descriptions to coexist in multiple languages.
Locale-Based Recommendations: Advanced analytics could suggest regional customizations to optimize user experience.
Facts:
- Multi-Language Support: Apache Superset 4.0.2 supports multiple languages, allowing organizations to cater to global audiences. Users can change the default language or set user-specific preferences.
- BABEL_DEFAULT_LOCALE Setting: The BABEL_DEFAULT_LOCALE configuration in the superset_config.py file is crucial for defining the platform’s default language.
- User Customization: Superset allows individual users to select their preferred language dynamically if the LANGUAGES setting is properly configured.
- Contributing Translations: Organizations can contribute translations via Apache Superset’s GitHub repository to expand language support.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Language localization improves user accessibility, enabling non-English speakers to navigate the platform effectively.
Final Words
Apache Superset 4.0.2’s language customization feature is a testament to its commitment to inclusivity and user-centric design. By allowing organizations to modify the default language and support multiple languages, it bridges gaps for global audiences. These updates not only enhance accessibility but also contribute to better user engagement, increased productivity, and broader adoption of the platform.
Localization isn’t just a feature—it’s a strategic tool for global outreach. By following best practices, organizations can leverage Apache Superset to create a seamless and culturally relevant experience for their diverse user base. As the platform evolves, we can anticipate even more robust localization features driven by advancements in AI and user feedback.
FAQs About Changing Default Language in Apache Superset
1. What file controls the default language settings in Apache Superset?
The superset_config.py file manages the default language settings and other localization configurations.
2. How do I set a different default language?
Modify the BABEL_DEFAULT_LOCALE setting in the superset_config.py file. For example, to set Spanish as the default language, add:
3. What are the supported language codes?
Some commonly used codes include:
- en: English
- es: Spanish
- fr: French
- zh: Chinese
A complete list can be found in the Apache Superset documentation or GitHub repository.
4. How can I enable user-specific language preferences?
To allow individual users to select their preferred language, configure the LANGUAGES setting in the superset_config.py file, e.g.:
5. What should I do if my changes don’t take effect?
Ensure the server is restarted after making changes to the superset_config.py file using the following commands:
6. Are all features translated into every language?
Not all languages have full translations for all features. Contributions to the Apache Superset project can help improve coverage.
7. Can I add new language packs?
Yes, you can contribute new translations via the Apache Superset GitHub repository. Once validated, these can be integrated into your environment.
8. What are common challenges when configuring language settings?
- Incomplete Translations: Some languages may lack comprehensive support.
- Server Errors: Syntax issues in the superset_config.py file may prevent the server from starting.
- Language Mismatch: Ensure that the BABEL_DEFAULT_LOCALE matches a supported language code.
9. Why is localization important for organizations?
Localization enhances accessibility, user satisfaction, and productivity by providing a platform that aligns with users’ linguistic and cultural preferences.
10. What future developments are expected in language customization for Apache Superset?
Advancements in AI may lead to features like real-time translations, hybrid multilingual dashboards, and geolocation-based language recommendations.
For more Information About Infromation visit: Sattaz